前言
英特尔公司发行的模型部署工具openvino™模型部署套件,可以实现在不同系统环境下运行,且发布的openvino™ 2023最新版目前已经支持os系统并同时支持在苹果m系列芯片上部署模型。在该项目中,我们将向大家展示如何在macos系统、m2芯片的macbook air电脑上,展示使用openvino™ c api 部署深度学习模型。
目录
英特尔发行版 openvino™ 工具套件基于 oneapi 而开发,可以加快高性能计算机视觉和深度学习视觉应用开发速度工具套件,适用于从边缘到云的各种英特尔平台上,帮助用户更快地将更准确的真实世界结果部署到生产系统中。通过简化的开发工作流程,openvino™ 可赋能开发者在现实世界中部署高性能应用程序和算法。
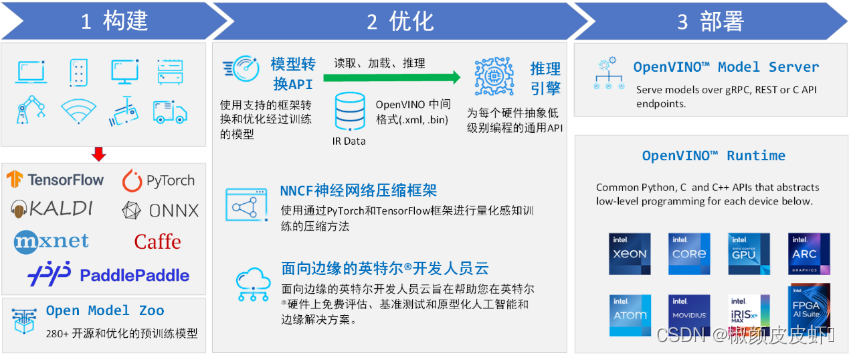
openvino™ 2023.2 于 2023 年 11 月 16 日发布,该工具包带来了挖掘生成人工智能全部潜力的新功能。更多的生成式 ai 覆盖和框架集成,以最大限度地减少代码更改,并且扩展了对直接 pytorch 模型转换的模型支持。支持更多新的模型,包括 llava、chatglm、bark 和 lcm 等著名模型。支持更广泛的大型语言模型(llm)和更多模型压缩技术,支持运行时推理支持以下 int4 模型压缩格式,通过神经网络压缩框架(nncf) 进行本机 int4 压缩等一系列新的功能。

通过openvino™d88尊龙官网手机app官网信息,我们可以看出,目前openvino™已经能够在苹果macos系统、m系列芯片上运行,这为使用macos系统的开发者提供了很好的工具。因此在此处,我们将在macos系统、m2芯片的macbook air电脑上,展示使用 openvino™ c api 部署深度学习模型的详细流程。
官方在发布版本中已经提供macos系统的编译库,因此在此处我们只需要下载官方编译库即可
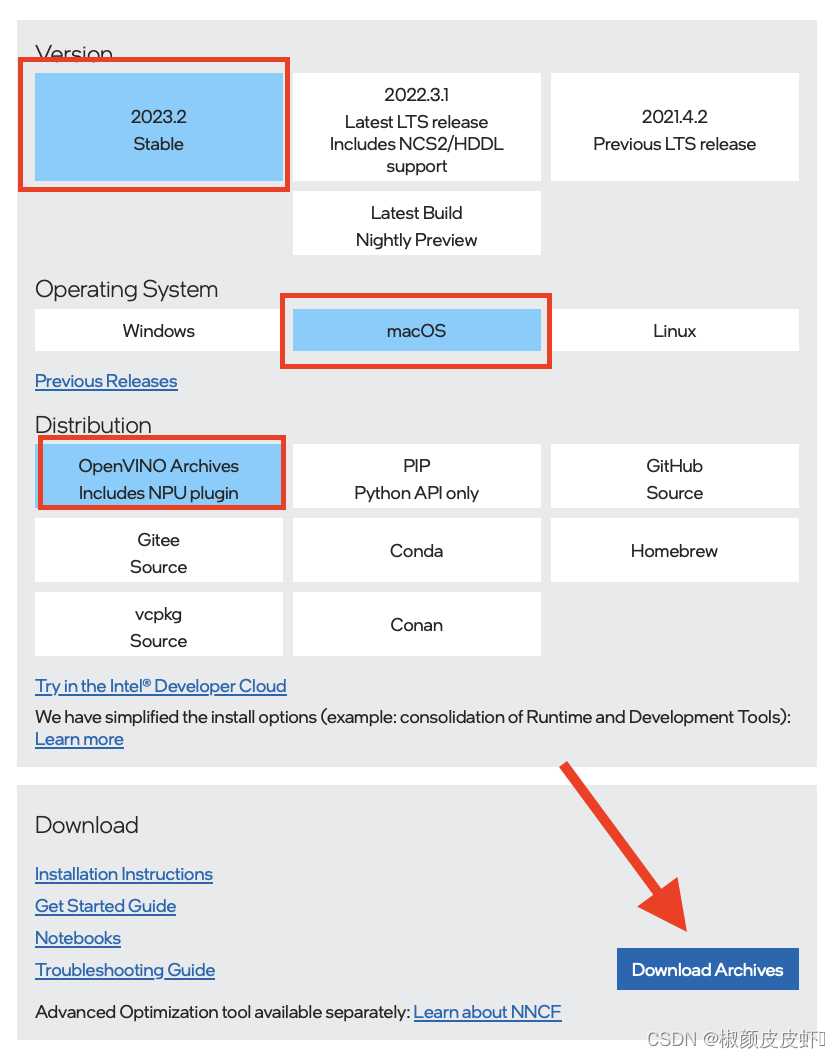
首先访问网站,依次选择版本号、操作系统、安装方式等内容,然后点击下载,如下图所示:
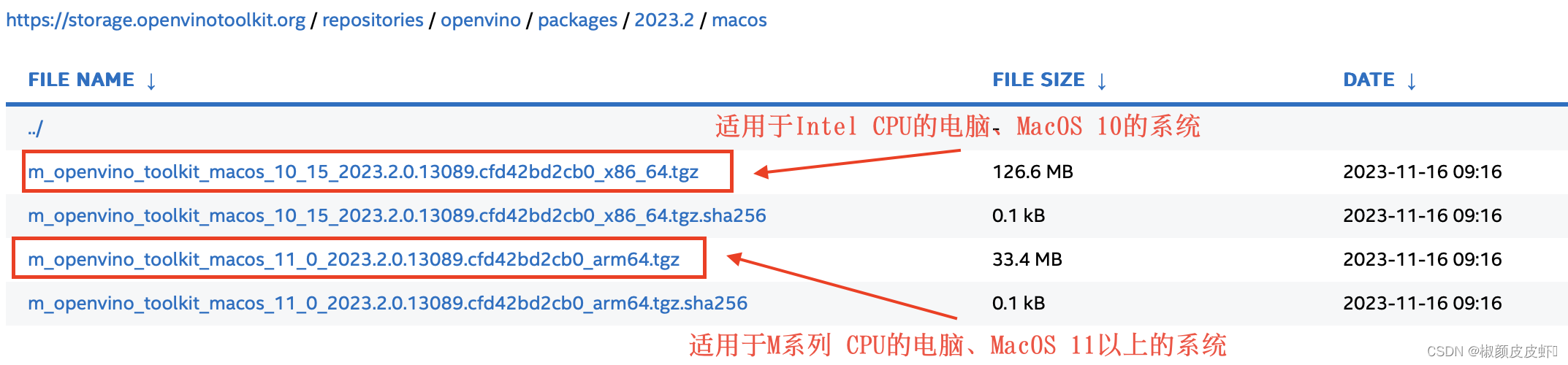
下面是官方编译的文件,此处主要提供了两个版本,一个是适用于苹果电脑之前的版本,主要是macos 10以及之前的版本系统并且使用的是intel cpu,另一个是使用了苹果的m系列芯片的新版本电脑,主要是macos 11 之后的系统。大家可以根据自己的电脑进行选择:
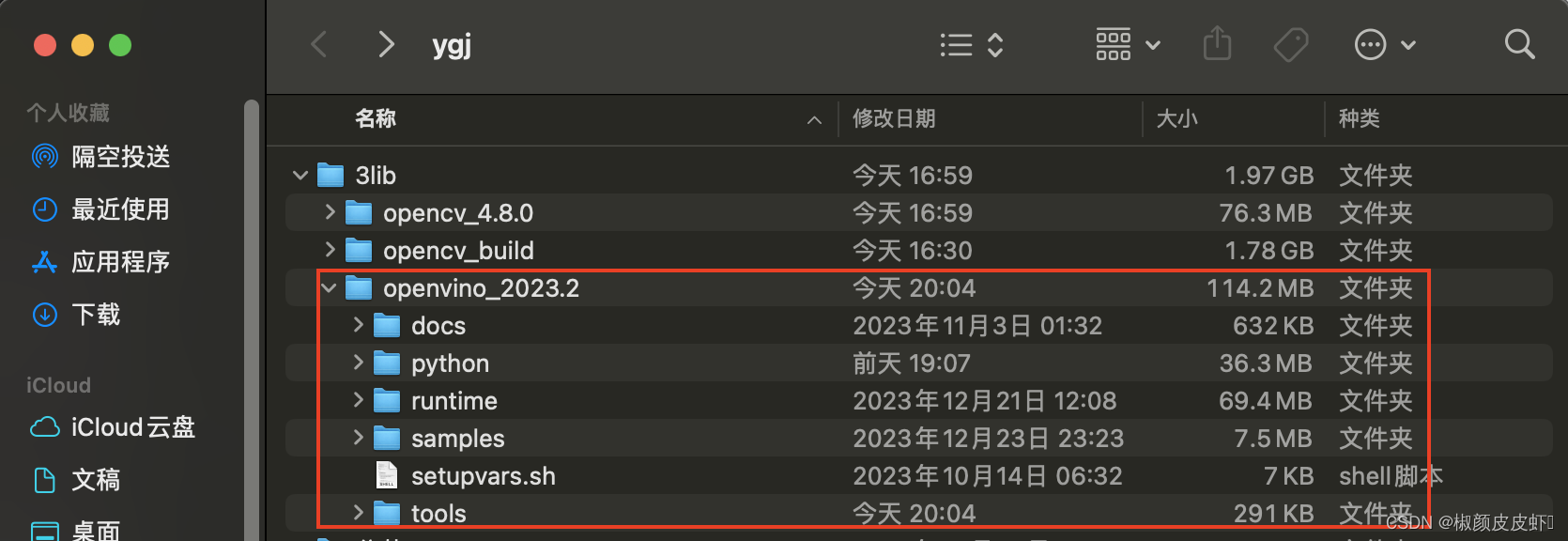
下载完后,将该文件解压到任意文件夹,在此处为了方便后续使用一集更新,将其解压到用户文件夹,如下图所示:
后续我们会使用cmake进行项目编译,因此我们此处无需再做其他的设置。
其他环境配置:
- macos:14.2.1
- cmake:3.28
- make:3.81
- 编译:visual studio code
- opencv:4.8.0
其他环境配置此处不做过多赘述,opencv环境安装可以参考下述文章实现:
此处我们以yolov8图片分类模型为例进行项目测试,由于该模型之前我们已经多次使用,所以在此处不在做耕作的阐述,具体代码如下所示:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "openvino/openvino.hpp" //openvino header file
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp" //opencv header file
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
ov::version version = ov::get_openvino_version();
std::cout << version.description << ": " << version.buildnumber << std::endl;
// -------- step 1. initialize openvino runtime core --------
ov::core core;
// -------- step 2. compile the model --------
auto compiled_model = core.compile_model("yolov8s-cls.xml", "cpu");
// -------- step 3. create an inference request --------
ov::inferrequest infer_request = compiled_model.create_infer_request();
// -------- step 4.read a picture file and do the preprocess --------
cv::mat img = cv::imread("image.jpg");
// preprocess the image
int col = img.cols;
int row = img.rows;
int _max = max(col, row);
cv::mat letterbox_img = cv::mat::zeros(_max, _max, cv_8uc3);
img.copyto(letterbox_img(cv::rect(0, 0, col, row)));
cv::mat blob = cv::dnn::blobfromimage(letterbox_img, 1.0 / 255.0, cv::size(224, 224), cv::scalar(), true);
// -------- step 5. feed the blob into the input node of the model -------
// get input port for model with one input
auto input_port = compiled_model.input();
std::cout << "the shape of input tensor:" << input_port.get_shape() << std::endl;
// create tensor from external memory
ov::tensor input_tensor(input_port.get_element_type(), input_port.get_shape(), blob.ptr(0));
// set input tensor for model with one input
infer_request.set_input_tensor(input_tensor);
// -------- step 6. start inference --------
infer_request.infer();
struct timeval start_time, end_time;
gettimeofday(&start_time,null);
infer_request.infer();
gettimeofday(&end_time,null);
// get the elapsed millisecond time
double elapsed_time = (end_time.tv_sec - start_time.tv_sec)*1000 (end_time.tv_usec - start_time.tv_usec)/1000;
// -------- step 7. get the inference result --------
auto output = infer_request.get_output_tensor(0);
auto output_shape = output.get_shape();
std::cout << "the shape of output tensor:" << output_shape << std::endl;
// -------- step 8. postprocess the result --------
float* output_buffer = output.data();
std::vector result(output_buffer, output_buffer output_shape[1]);
auto max_idx = std::max_element(result.begin(), result.end());
int class_id = max_idx - result.begin();
float score = *max_idx;
std::cout << "class id:" << class_id << " score:" <
在该代码中,主要是获取openvino™版本信息,然后按照模型部署流程部署测试了yolov8图片分类模型,并打印输出结果以及推理时间。
在该项目中通过cmake编译项目,定义的cmakelists.txt文件如下所示:
cmake_minimum_required(version 3.28)
project(test_openvino)
set(opencv_dir /users/ygj/3lib/opencv_4.8.0/lib/cmake/opencv4)
find_package(opencv required)
message(status "opencv_dir = ${opencv_dir}")
message(status "opencv_include_dirs = ${opencv_include_dirs}")
message(status "opencv_libs = ${opencv_libs}")
set(openvino_dir /users/ygj/3lib/openvino_2023.2/runtime/cmake)
set(openvino_libs "/users/ygj/3lib/openvino_2023.2/runtime/lib/arm64/release/libopenvino.2320.dylib")
set(cmake_cxx_flags "${cmake_cxx_flags} -std=c 11")
include_directories(
/users/ygj/3lib/openvino_2023.2/runtime/include
${opencv_include_dirs}
)
add_executable(test_openvino test_openvino.cpp )
target_link_libraries(test_openvino ${openvino_libs} ${opencv_libs})
在这个cmakelists文件中,需要同时配置opencv以及openvino这两个依赖库,具体编译以及配置方式参考cmake手册。
接下来就可以项目编译了,在终端中输入一下命令,就可以进行项目配置了,输出结果如下所示:
cmake .
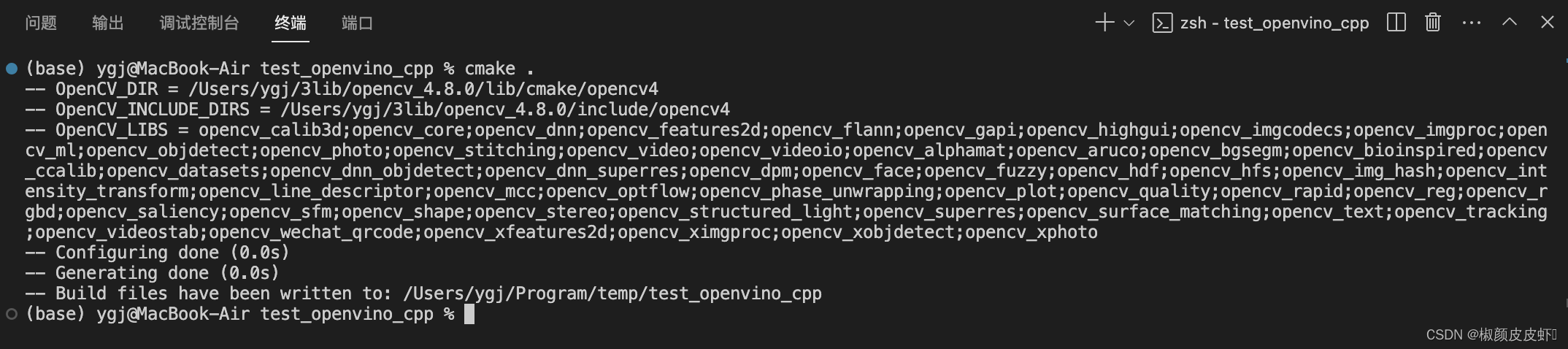
接下来就是进行项目编译,cmake编译后会生成makefile文件,之后就可以运行make命令进行项目最后的编译,然后就可以直接运行生成的项目文件,如下所示:
make
./test_openvino
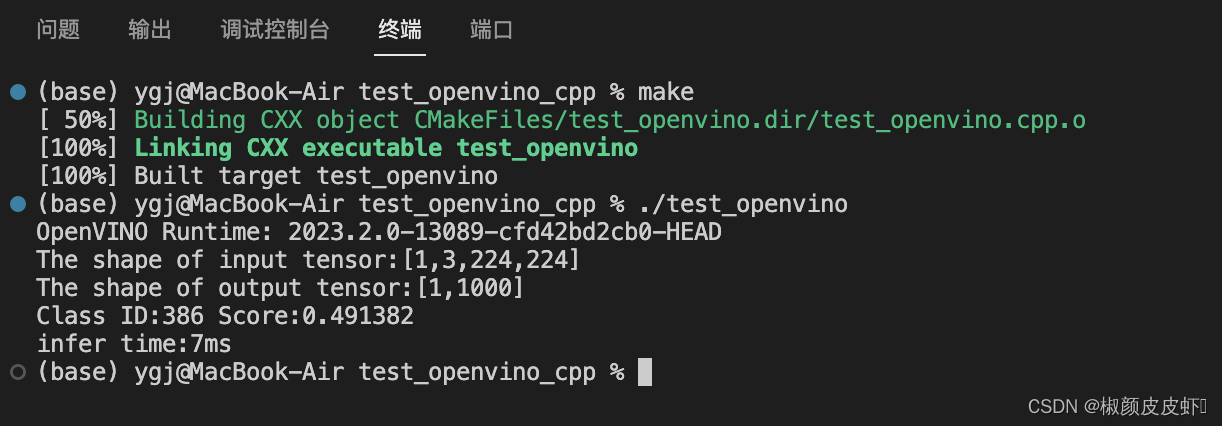
上图中展示了项目最后运行结果,可以看出,此处使用的模型输入大小为[1,3,224,224],输出大小为[1,1000],识别结果class id=386,查看分类结果字典,图片识别结果与图片一致;模型的推理时间为:7ms。
该项目中,我们在macos 14.2.1 系统、m2芯片的 macbook air 电脑上,成功使用openvino™ c api 部署了yolov8图片分类深度学习模型,并详细演示了openvino™ c api在苹果电脑上使用与配置流程,为使用macos系统的开发者提供了很好的范例与参考。

