angularjs 的生命周期和基础语法
1. 使用步骤
// 1. 要使用哪个钩子函数,就先引入
import { oninit } from ...
// 2. 再实现
export class 组件名 implements onint...
// 3. 再使用
ngoninit(){
....
}
2. 生命周期钩子函数

- ngonchanges()
当输入属性的值发生变化时调用。
在组件被创建并且输入属性绑定发生变化时调用。首次调用一定会发生在ngoninit()之前。
- ngoninit()
在组件初始化时调用。
通常用于执行初始化逻辑,例如获取初始数据。在第一轮 ngonchanges()完成之后调用,只调用一次。
- ngdocheck()
当 angular 安排检查时调用。
用于自定义的变更检测逻辑,通常与 changedetectorref 结合使用。在ngonchanges()和ngoninit()之后。
- ngaftercontentinit()
在组件内容投影完成后调用。
用于执行需要在组件内容初始化后执行的逻辑。第一次ngdocheck()之后调用,只调用一次,只适用于组件。
- ngaftercontentchecked()
在每次 angular 完成对组件内容的检查之后调用。
用于执行在内容检查之后需要执行的逻辑。ngaftercontentinit()和每次ngdocheck()之后调用,只适用于组件。
- ngafterviewinit()
在组件视图初始化完成后调用。
用于执行需要访问视图的初始化逻辑。第一次ngaftercontentchecked()之后调用,只调用一次,只适合组件。
- ngafterviewchecked()
在每次 angular 完成对组件视图的检查之后调用。
用于执行在视图检查之后需要执行的逻辑。ngafterviewinit()和每次ngaftercontentchecked()之后调用,只适合组件。
- ngondestroy()
在组件销毁时调用。
通常用于清理资源,取消订阅等。
3. 点击事件
将 app.component.html 文件内容清空,只保留
在 app.component.html 中添加button标签,并按下面代码添加点击事件
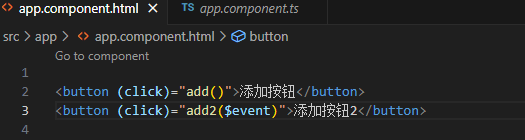
import { commonmodule } from '@angular/common';
import { component } from '@angular/core';
import { routeroutlet } from '@angular/router';
import { formsmodule } from '@angular/forms';
@component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [commonmodule,routeroutlet,formsmodule],
templateurl: './app.component.html',
styleurl: './app.component.css'
})
export class appcomponent {
title = 'testdemo';
add(){
alert('这是一个测试框!')
}
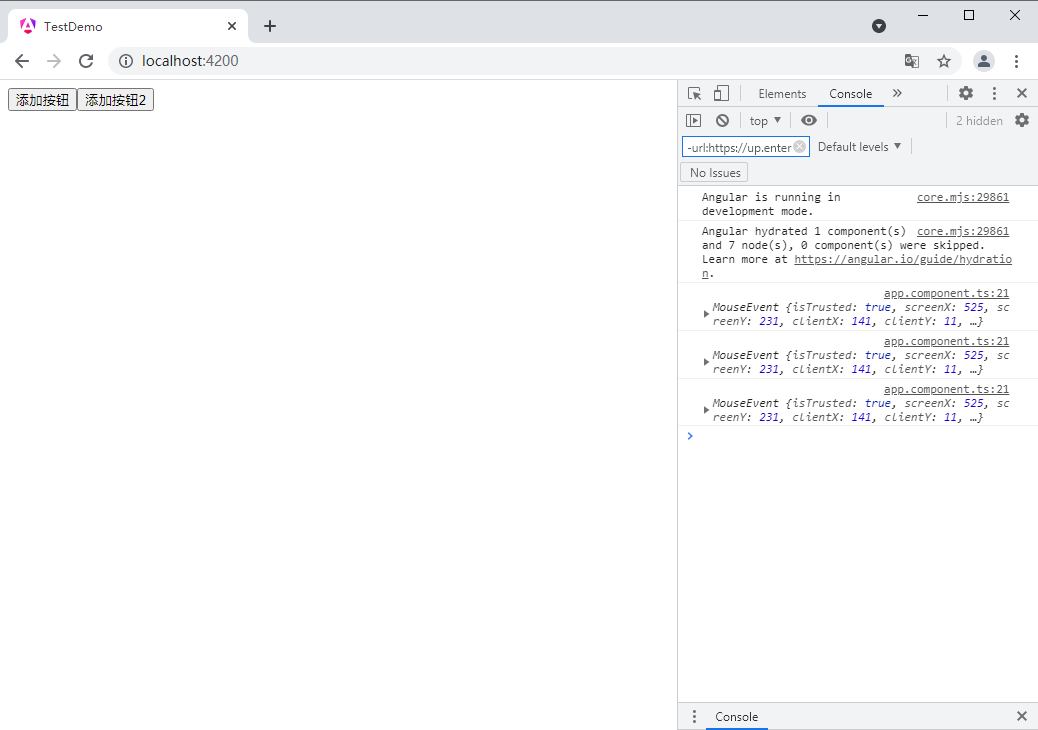
add2(e:mouseevent){
console.log(e)
}
}
按钮1
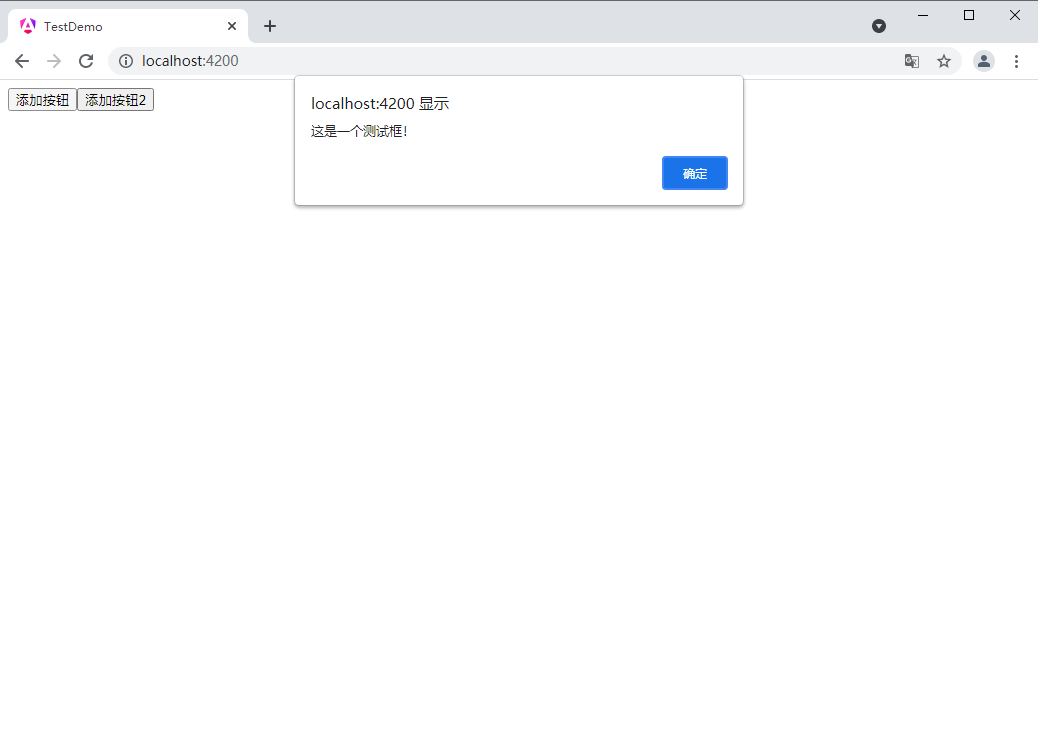
按钮2
4. if 语句
1. if 形式
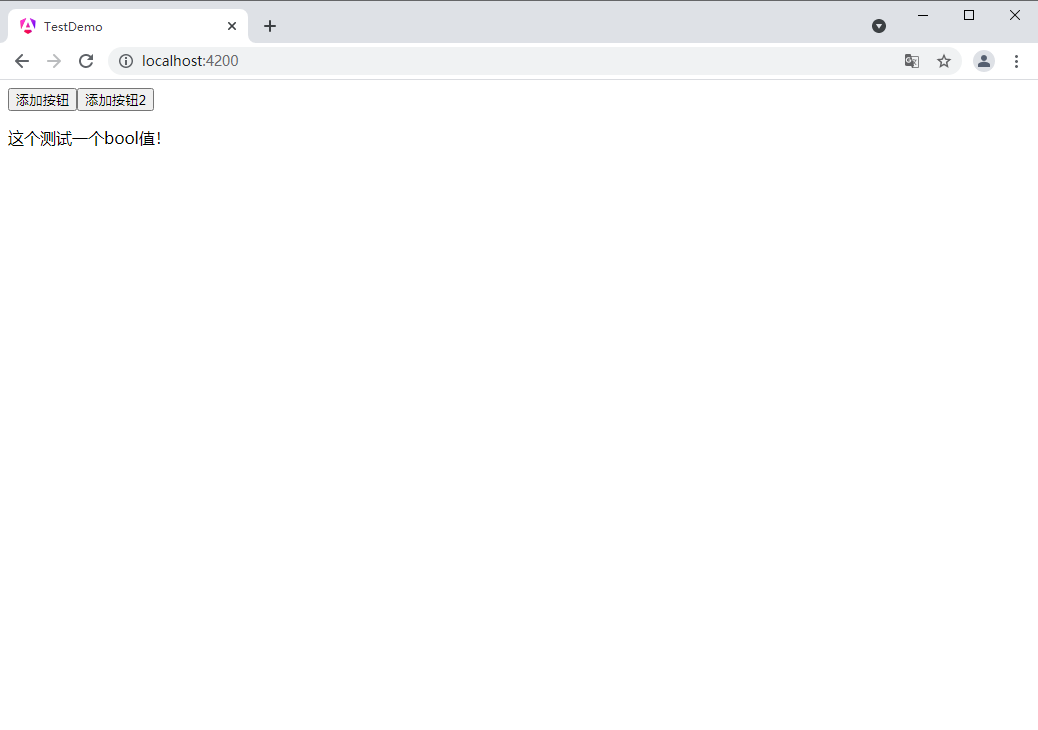
在 app.component.ts 中定义变量 isshow
isshow : boolean = true
app.component.html 中写 if 判断
这个测试一个bool值!
2. if else 形式
import { commonmodule } from '@angular/common';
import { component } from '@angular/core';
import { routeroutlet } from '@angular/router';
import { formsmodule } from '@angular/forms';
@component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [commonmodule,routeroutlet,formsmodule],
templateurl: './app.component.html',
styleurl: './app.component.css'
})
export class appcomponent {
title = 'testdemo';
add(){
alert('这是一个测试框!')
}
add2(e:mouseevent){
console.log(e)
}
isshow : boolean = true
isshow2 : boolean = true
changeshow(){
this.isshow2 = !this.isshow2
}
}
app.component.html
这个测试一个bool值!
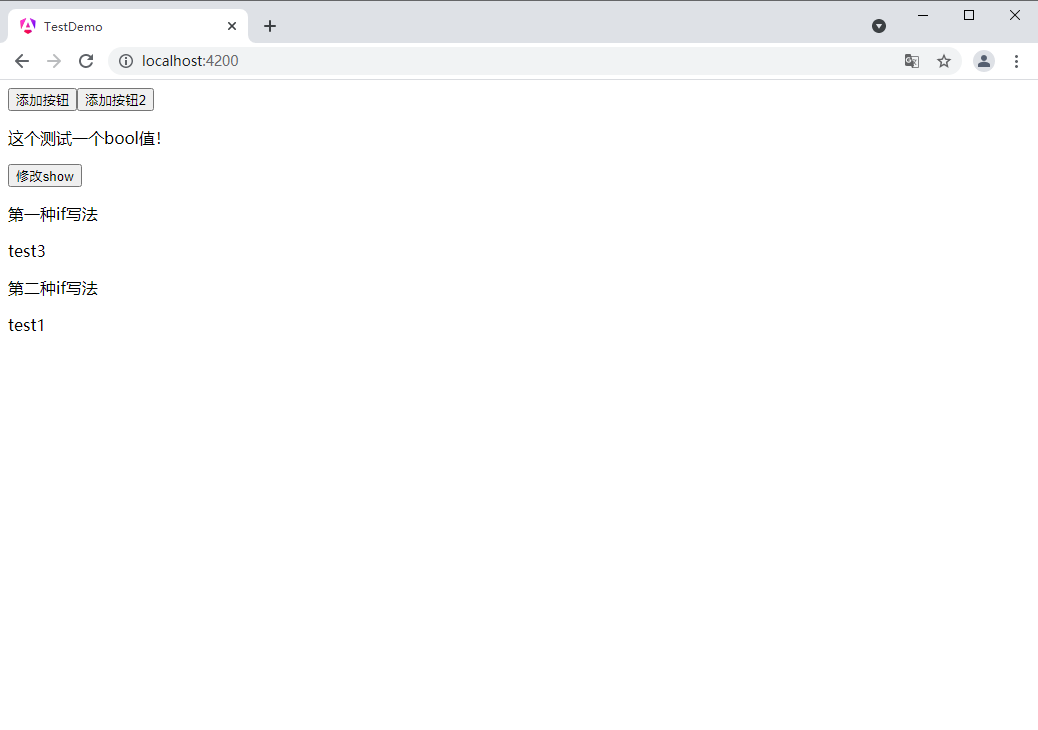
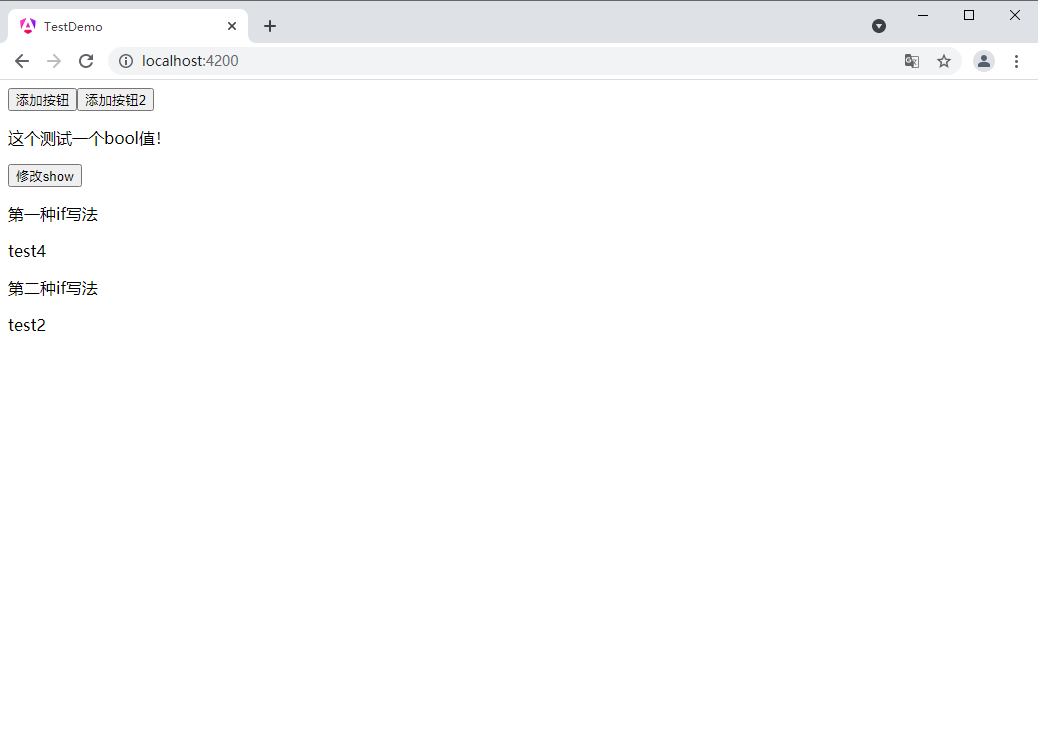
第一种if写法
@if (isshow2) {test3
} @else {test4
}第二种if写法
test1
test2
点击按钮
5. for 语句
app.component.ts
import { commonmodule } from '@angular/common';
import { component } from '@angular/core';
import { routeroutlet } from '@angular/router';
import { formsmodule } from '@angular/forms';
@component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [commonmodule,routeroutlet,formsmodule],
templateurl: './app.component.html',
styleurl: './app.component.css'
})
export class appcomponent {
title = 'testdemo';
add(){
alert('这是一个测试框!')
}
add2(e:mouseevent){
console.log(e)
}
isshow : boolean = true
isshow2 : boolean = true
changeshow(){
this.isshow2 = !this.isshow2
}
mylist:array = [
'死生契阔,与子成说',
'执子之手,与子偕老',
'我心匪石,不可转也',
'有一美人兮,见之不忘'
]
}
app.component.html
这个测试一个bool值!
第一种if写法
@if (isshow2) {test3
} @else {test4
}第二种if写法
test1
test2
---------------------------
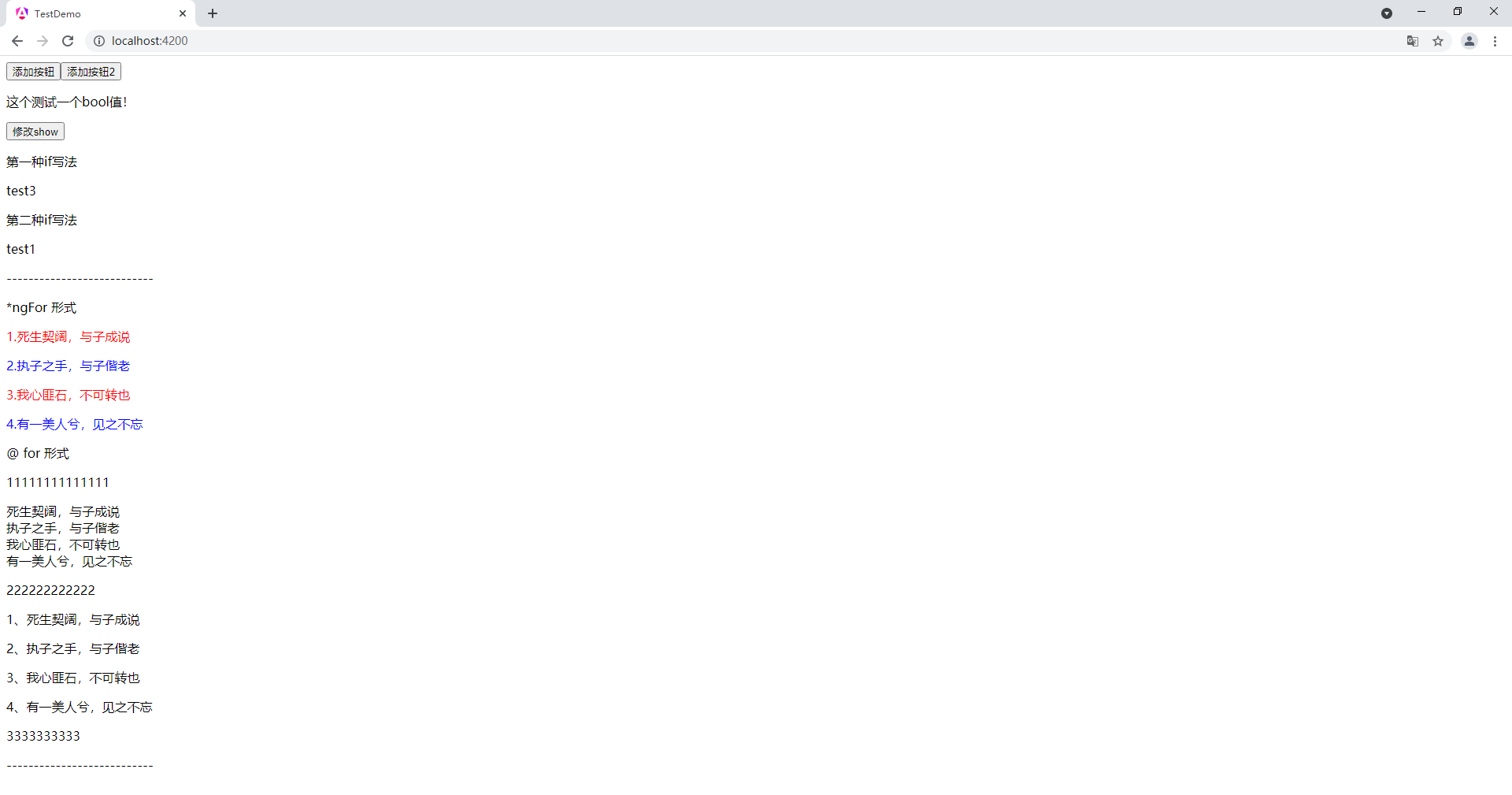
*ngfor 形式
{{i 1}}.{{item}}
@ for 形式
11111111111111
@for (item of mylist; track item) {{{item}}}@empty { empty mylist }222222222222
@for (item of mylist; track $index) {{{$index 1}}、{{item}}
}3333333333
---------------------------
6. switch 语句
app.component.ts
import { commonmodule } from '@angular/common';
import { component } from '@angular/core';
import { routeroutlet } from '@angular/router';
import { formsmodule } from '@angular/forms';
@component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [commonmodule,routeroutlet,formsmodule],
templateurl: './app.component.html',
styleurl: './app.component.css'
})
export class appcomponent {
title = 'testdemo';
add(){
alert('这是一个测试框!')
}
add2(e:mouseevent){
console.log(e)
}
isshow : boolean = true
isshow2 : boolean = true
changeshow(){
this.isshow2 = !this.isshow2
}
mylist:array = [
'死生契阔,与子成说',
'执子之手,与子偕老',
'我心匪石,不可转也',
'有一美人兮,见之不忘'
]
author:number = 0
changauthor() {
this.author = this.author 1
console.log(this.author)
}
}
app.component.html
这个测试一个bool值!
第一种if写法
@if (isshow2) {test3
} @else {test4
}第二种if写法
test1
test2
---------------------------
*ngfor 形式
{{i 1}}.{{item}}
@ for 形式
11111111111111
@for (item of mylist; track item) {{{item}}}@empty { empty mylist }222222222222
@for (item of mylist; track $index) {{{$index 1}}、{{item}}
}3333333333
---------------------------
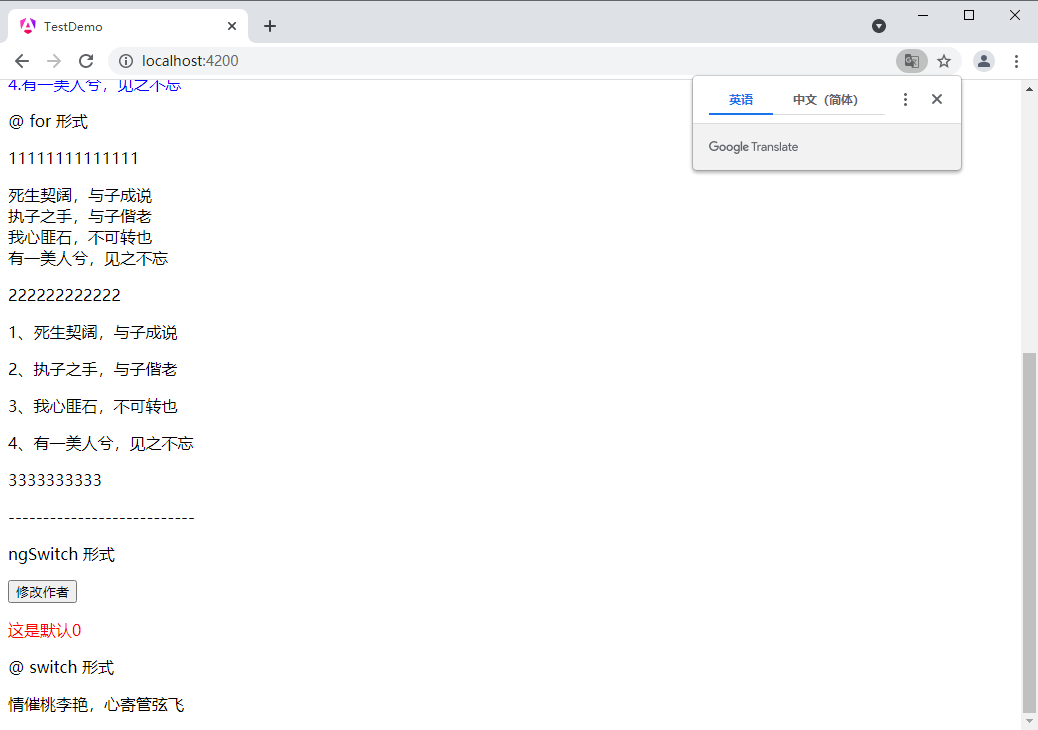
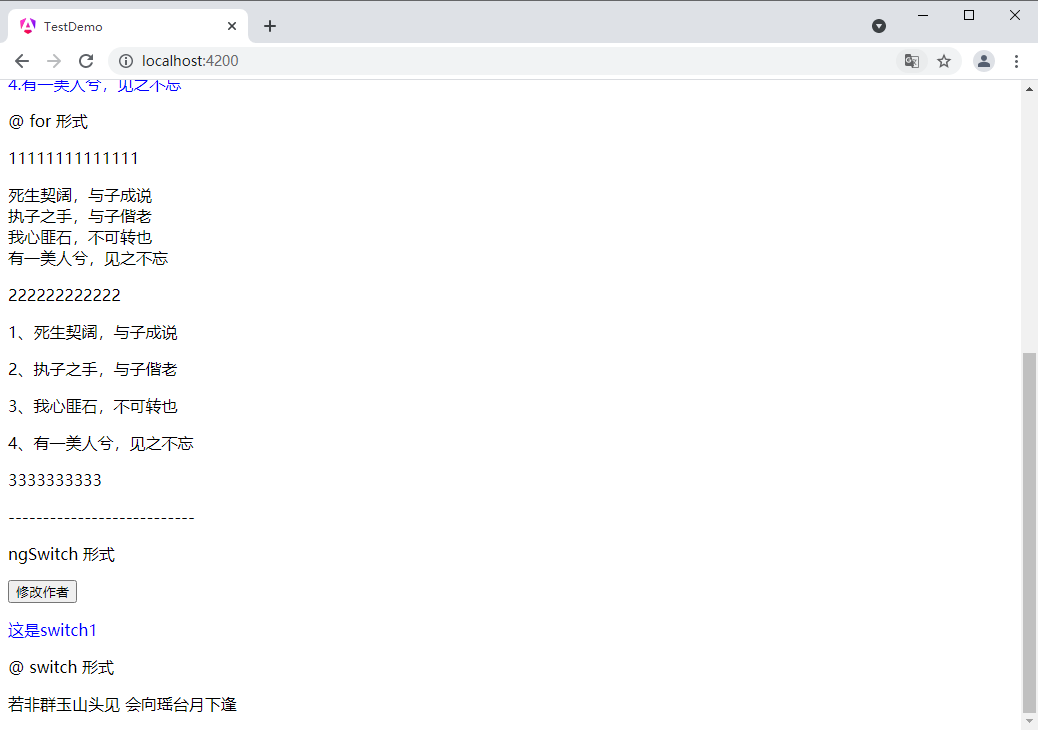
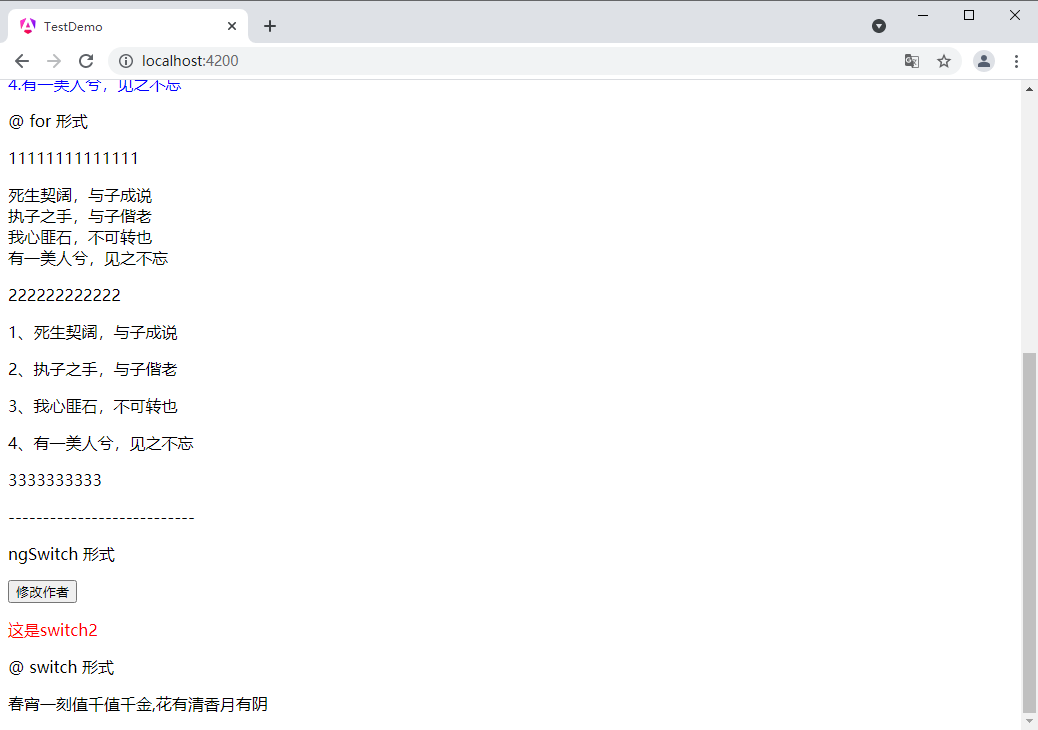
ngswitch 形式
这是switch1
这是switch2
这是switch3
这是默认{{author}}
@ switch 形式
@switch (author) { @case (1) {若非群玉山头见 会向瑶台月下逢
} @case (2) {春宵一刻值千值千金,花有清香月有阴
} @default {情催桃李艳,心寄管弦飞
} }
点击按钮
7. 双向数据绑定
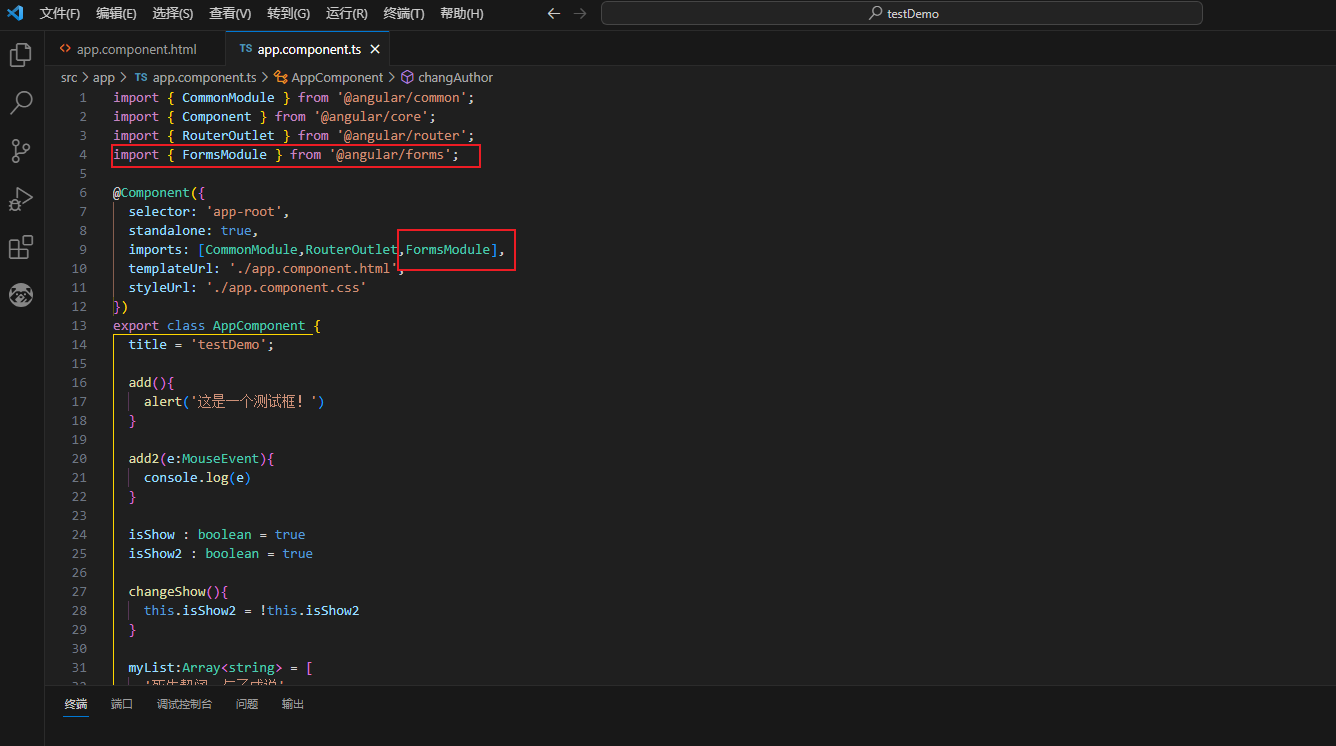
实现双向数据绑定,需要引入angular 内置的 formsmodule 模块
在 app.component.ts 文件中引入
import { formsmodule } from '@angular/forms';
并在 @component 的 import 中添加 formsmodule
app.component.ts
import { commonmodule } from '@angular/common';
import { component } from '@angular/core';
import { routeroutlet } from '@angular/router';
import { formsmodule } from '@angular/forms';
@component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [commonmodule,routeroutlet,formsmodule],
templateurl: './app.component.html',
styleurl: './app.component.css'
})
export class appcomponent {
title = 'testdemo';
add(){
alert('这是一个测试框!')
}
add2(e:mouseevent){
console.log(e)
}
isshow : boolean = true
isshow2 : boolean = true
changeshow(){
this.isshow2 = !this.isshow2
}
mylist:array = [
'死生契阔,与子成说',
'执子之手,与子偕老',
'我心匪石,不可转也',
'有一美人兮,见之不忘'
]
author:number = 0
changauthor() {
this.author = this.author 1
console.log(this.author)
}
teststring:string='test001'
}
app.component.html
这个测试一个bool值!
第一种if写法
@if (isshow2) {test3
} @else {test4
}第二种if写法
test1
test2
---------------------------
*ngfor 形式
{{i 1}}.{{item}}
@ for 形式
11111111111111
@for (item of mylist; track item) {{{item}}}@empty { empty mylist }222222222222
@for (item of mylist; track $index) {{{$index 1}}、{{item}}
}3333333333
---------------------------
ngswitch 形式
这是switch1
这是switch2
这是switch3
这是默认{{author}}
@ switch 形式
@switch (author) { @case (1) {若非群玉山头见 会向瑶台月下逢
} @case (2) {春宵一刻值千值千金,花有清香月有阴
} @default {情催桃李艳,心寄管弦飞
} } {{teststring}} {{teststring}}
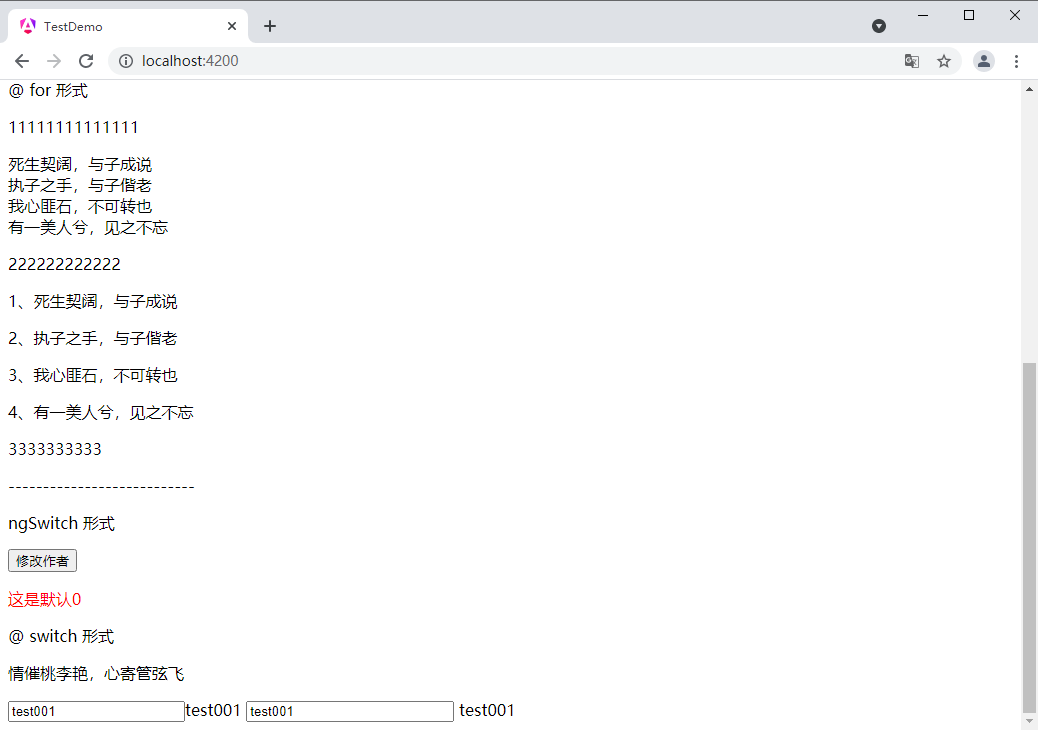
输入之后
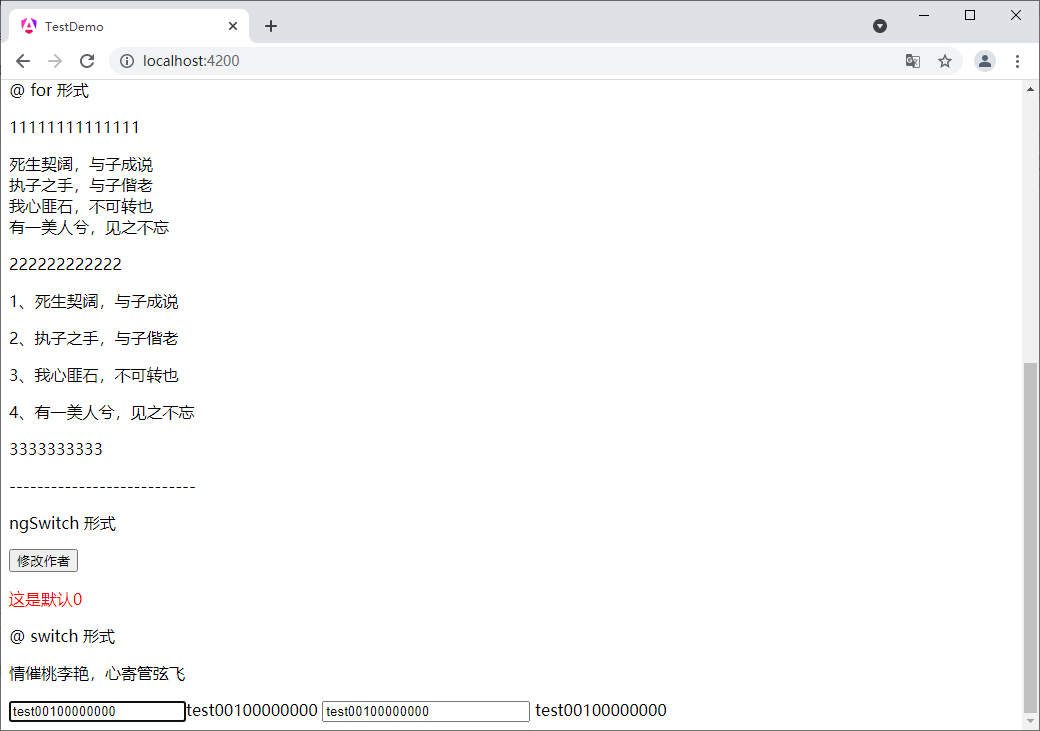
这里解释一下
[(ngmodel)] 实际上展开为:
这里有两个关键部分:
- [ngmodel]=“teststring”:这是一个属性绑定,它将 ngmodel 的值设置为组件的 teststring属性。这意味着当 teststring 在组件类中改变时,ngmodel 的值(即输入框的值)也会自动更新。
- (ngmodelchange)=“teststring=$event”:这是一个事件绑定,它监听 ngmodelchange事件。当输入框的值改变时,这个事件会被触发,并将新的值作为 $event 传递给事件处理器。事件处理器将 $event 的值赋给teststring,从而实现了从视图到组件的数据更新。
所以,当你在输入框中键入文本时,这个文本会立即反映到 teststring 属性上,反之亦然,如果你在组件类中改变 teststring 的值,输入框的内容也会相应更新。

